Pollinator Bees Need to be Protected if We Want Our Planet to Survive 
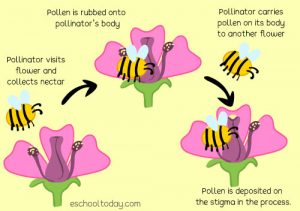
Bees may seem small, but the impact they have on the ecosystem is enormous. Bees account for the survival of 80% of all plants on Earth. Their pollinating skills are what allow plants to repopulate in such efficient ways that cover vast swaths of land. Bees support the agricultural system greatly by pollinating crops such as nuts, fruits, and vegetables. The pollination process plays a significant role in the survival of 100 types of crops. The pollination process is demonstrated in the diagram below.
Without the help of the bee’s crops and livestock would suffer and die out slowly. This means that we humans would not have our main source of meat or vegetables. Bees are responsible for increasing the crop yield of around 90 crops by at least 30%. Without this abundance of food, the number of accessible crops would decrease causing the prices of the crops left to skyrocket.
If bees became extinct, the human race would soon follow. Bees have been declared the most invaluable species by the annual Earthwatch debate in 2008. Without bees, the majority of human food sources would die out. Our access to many necessary medicines would also become limited as the plants that are used as ingredients start to become endangered. We also use cotton, one of the main crops that benefitted from bee pollination, in many aspects of our lives including bandages and clothing. The loss of bees would throw the whole ecosystem out of balance resulting in many species of plants and animals becoming extinct. Carnivores and Omnivores alike would starve resulting in a mass extinction event. While there are other pollinators, bees make up the majority of the work because there are over 20,000 species of bees working at pollinating the world.
There are many threats to the survival of bees, but the most prevalent are pesticides, parasites, habitat loss, and lack of genetic diversity. To begin, Bees are typically kept in captivity on farmland. This land is heavily coated in pesticides containing harsh chemicals that are harmful to the life of the bees. Bees are especially affected because they travel from plant to plant to pollinate which exposes them to pesticides. Secondly, bees are vulnerable to habitat loss due to climate change, deforestation, and farmers deciding to stop taking care of bees. Bees construct an elaborate hive that is designed to benefit a bee’s lifestyle. Losing these homes causes bees to become vulnerable to outside threats that they would typically be protected from inside a hive.
The next threat bees face is the lack of genetic diversity. Bees in the wild are able to intermingle and create subspecies, but bees in captivity are all very genetically similar. Due to the high levels of bee populations living in captivity, many hives have been interbreeding for years which results in a high genetic similarity amongst the bees. This is a threat to their survival because if a disease comes through, the genetically similar bees will all have the same level of vulnerability where the genetically diverse hives will have a higher chance of survival. Finally, bees are susceptible to parasites, especially one known as a Varroa Destructor. This parasite is depicted in the diagram below. The parasite attaches itself to the larvae of the bee before the larvae’s cove is sealed over with beeswax. The parasite lays eggs and feeds on the larvae until the larvae becomes a pupa and breaks through the seal. This pupa is now a bee that is infected with the Varroa Destructor and soon dies. The destructor continues this cycle until the whole hive is suffering and on the brink of death.
While bees face many threats, there are ways that we can combat their endangerment. One easy way to help out bees is by building a garden full of pollinator plants. This will provide a safe space for the bees to pollinate and live. These gardens will provide an abundance of nutritious food sources for the bees. If you want to be even more involved in providing a safe space for bees, you could add a little bee house to your garden. A few types of bee homes are pictured below. The main qualification for a bee house is to have small tube-like structures for a bee to make their home in. These structures are typically made out of wood. A second way to help out the bees is by actively reducing chemical uses while landscaping and gardening. An uncontaminated ecosystem will thrive without the threat of dying from chemicals. The biodiversity will increase which will, in turn, allow more pollination to happen. Finally, you can create a bee bath for the bees to land in and drink after a hard day’s work of pollinating. To do so you can fill a birdbath or bowl with a shallow amount of water. You will need to place pebbles or rocks in the water for the bees to land on so they will not drown. If you want to spice it up a bit you could add some sugar to the water to energize the bees, but this may also attract unwanted visitors like ants or flies.
Bees are an essential cog in the ecosystem. They are often overlooked and forgotten, but we need to work toward helping them survive. The only way we are going to have a planet to live on is if we keep the bees alive. Practicing sustainable gardening will help to create a safe environment for bees to do their work in. These small chubby bugs may not look like much, but they are necessary to the survival of the majority of the Earth’s living creatures.
Sources Used:
10 Ways to Save the Bees. 2 Dec. 2020, thebeeconservancy.org/10-ways-to-save-the-bees/.
“Why Bees Are the Most Invaluable Species.” The Guardian, Guardian News and Media, 21 Nov. 2008, www.theguardian.com/environment/blog/2008/nov/21/wildlife-endangeredspecies.













 These delicious looking fruits, which contain 73% water, 15% fat, 8.5% carbohydrates, mostly fibres and 2% protein, are one of the highest demanding products in our world. Due to the demands, it becomes multibillion-dollar industrial products.
These delicious looking fruits, which contain 73% water, 15% fat, 8.5% carbohydrates, mostly fibres and 2% protein, are one of the highest demanding products in our world. Due to the demands, it becomes multibillion-dollar industrial products. The fruit is harvested in Chile, Mexico, and California. The profits from these fruits have made many industries, business corporations, and investors to go to the extreme of producing and selling them on a large market scale. And the consequences are the suffering of carbon footprint, deforestation, droughts, business instability and many more.
The fruit is harvested in Chile, Mexico, and California. The profits from these fruits have made many industries, business corporations, and investors to go to the extreme of producing and selling them on a large market scale. And the consequences are the suffering of carbon footprint, deforestation, droughts, business instability and many more.









 event on behalf of one of the clubs I am in, Furman Creative Collaborative/TEDx. Being the ambitious and overcommitting person I am, I said YES. Now I am sure by now you find yourself wondering why all of this is important, but here it is. IDEAS into ACTIONS!
event on behalf of one of the clubs I am in, Furman Creative Collaborative/TEDx. Being the ambitious and overcommitting person I am, I said YES. Now I am sure by now you find yourself wondering why all of this is important, but here it is. IDEAS into ACTIONS!